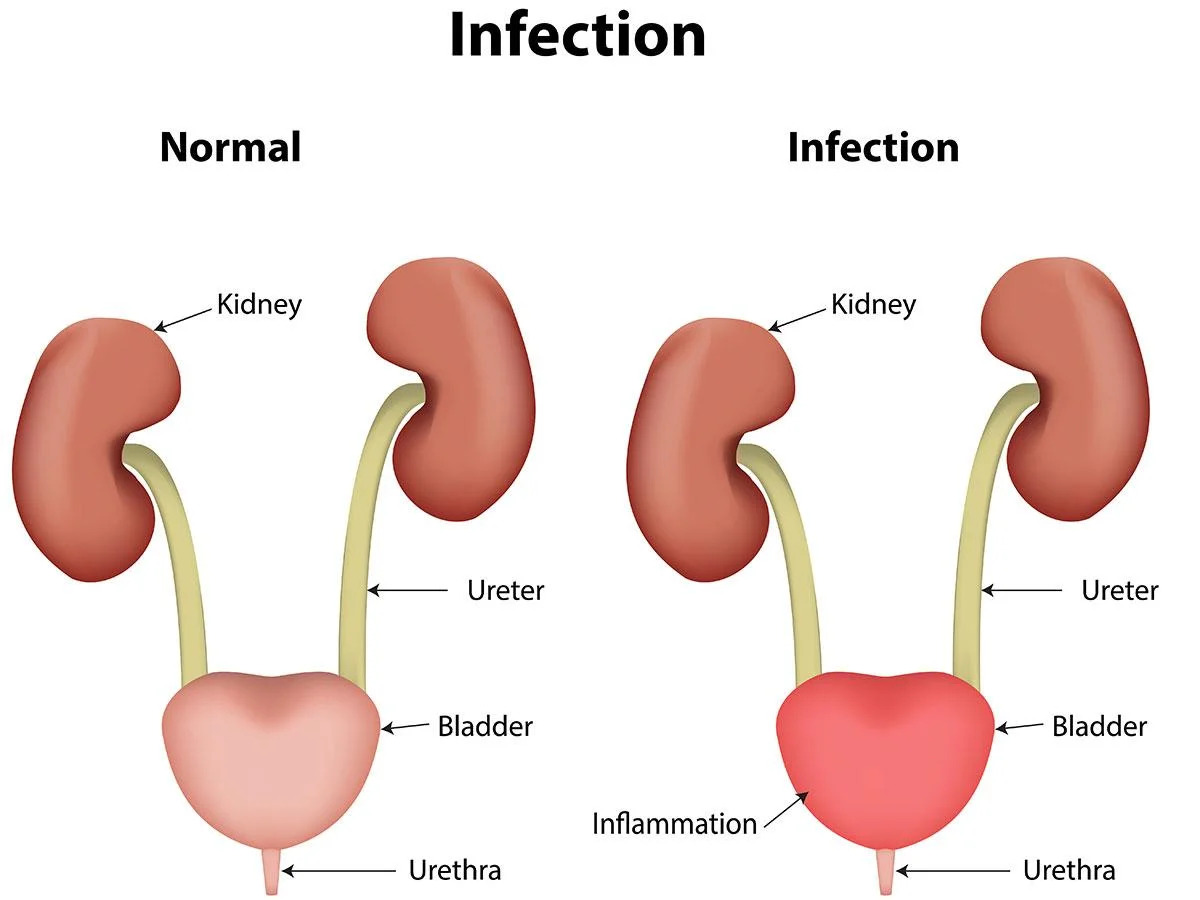
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is an infection of the urinary tract. The urinary tract can be divided into the upper urinary tract and the lower urinary tract. The upper urinary tract consists of the kidneys and the ureters, and the lower urinary tract consists of the bladder and the urethra. Normally, urine moves through your urinary system without any contamination. However, bacteria can get into the urinary system from outside of the body, causing problems like infection and inflammation. Recurrent infections can occur, especially in women, especially if they go undertreated. Permanent kidney damage from an acute or chronic kidney infection (pyelonephritis) can ensue due to an untreated UTI. It can present in people of all ages.
Signs and symptoms:
The symptoms of a UTI can depend on age, gender, the presence of a catheter, and what part of the urinary tract has been infected.
Common symptoms of a UTI include:
- strong and frequent urge to urinate
- cloudy, bloody, or strong-smelling urine
- pain or a burning sensation when urinating
- nausea and vomiting
- muscle aches and abdominal pains
People with catheters may only experience fever as a symptom, making diagnosis more difficult.
When to see a doctor?
Most healthcare providers recommend contacting your doctor as soon as you notice bladder infection symptoms or urinary tract infection symptoms. You should also see your healthcare provider if you get frequent UTIs. If you have three or more urinary tract infections in 12 months, call your doctor.
پیشاب کی نالی کا انفیکشن (UTI):
پیشاب کی نالی کو دو حصوں میں تقسیم کیا جاسکتا ہے۔ اس کا بالائی حصہ گردوں اور پیشاب کی نالیوں (ureters) پر مشتمل ہوتا ہے اور نچلا حصہ مثانے اور پیشاب باہر نکالنے والی نالی (urethra) پر مشتمل ہوتا ہے۔ عام طور پر ، پیشاب میں جراثیم نہیں پائے جاتے۔ تاہم ، بیکٹیریا جسم کے باہر سے پیشاب کے نظام میں داخل ہو سکتے ہیں ، جس سے انفیکشن اور سوزش جیسے مسائل پیدا ہوتے ہیں۔ خواتین میں اکثر بار بار انفیکشن ہوسکتا ہے ، خاص طور پر اگر علاج نامکمل رہ جائے ۔ بار بار گردے کے انفیکشن (پائلونفرائٹس) سے گردے کو دائمی نقصان پہنچ سکتا ہے اگر صحیح سے علاج نہ کیا گیا ہو۔ یہ ہر عمر کے لوگوں میں پایا جاتا ہے۔
نشانات و علامات
یو ٹی آئی کی علامات عمر ، جنس ، کیتھیٹر کی موجودگی ، اور پیشاب کی نالی کا کون سا حصہ متاثر ہوا ہے، ان پر منحصر ہے۔ یو ٹی آئی کی عام علامات میں شامل ہیں:
- پیشاب کرنے کی شدید اور بار بار خواہش۔
- خونی ، یا تیز خوشبودار پیشاب۔
- پیشاب کرتے وقت درد یا جلن۔
- متلی اور قےکی شکایت۔
- پٹھوں میں درد اور پیٹ میں درد
- کیتھیٹر والے لوگوں میں صرف بخار ہی ایک علامت کے طور پر ظاہر ہوتا ہے ، جس سے تشخیص زیادہ مشکل ہو جاتی ہے۔
ڈاکٹر سے کب ملنا ہے:
جیسے ہی آپ کو پیشاب کی نالی یا مثانے کے انفیکشن کی علامات ظاہر ہوں آپ فوری طور پر ڈاکٹر سے مشورہ کریں ۔ اگر آپ کو بار بار یو ٹی آئی ہو تو بھی آپ کو اپنے ڈاکٹر کو دکھانا چاہیے۔ اگر آپ کو 12 ماہ میں تین بار یا اس سے زیادہ پیشاب کی نالی میں انفیکشن ہو تو اپنے ڈاکٹر سے رجوع کریں۔
Doctors to consult (Urologist):
Asst.Prof. Dr. Mohsin Naveed, Dr. Nina Munir, Dr Shahid Hussain, Dr. Zafar Abbas
Note: Click the Doctor's name to make an appointment.
Reference:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-tract-infection/symptoms-causes/syc-20353447
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/189953#_noHeaderPrefixedContent
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9135-urinary-tract-infections