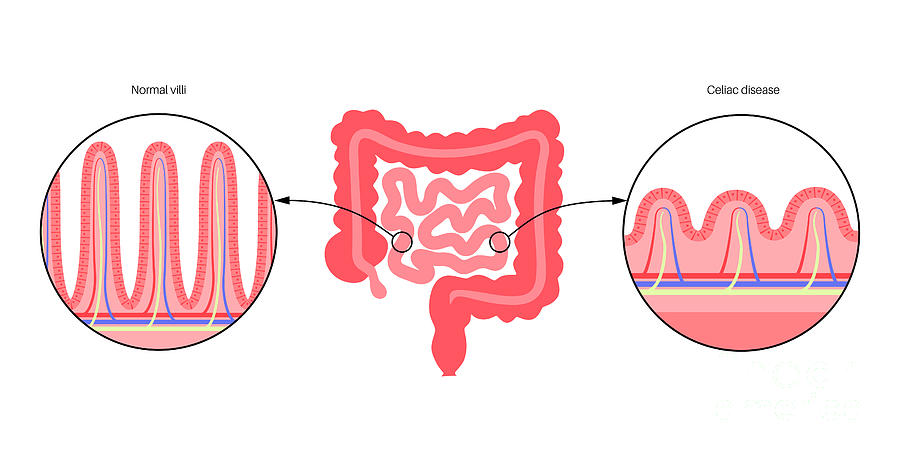
Coeliac disease is caused by an adverse reaction to gluten, which is a dietary protein found in 3 types of cereal: wheat, barley, and rye. Gluten is found in any food that contains those cereals. Gluten causes inflammation (swelling) in the intestines and damages the villi, the hair-like structures on the lining of the small intestine. Nutrients from food are absorbed by the villi. If the villi are damaged, the person cannot absorb nutrients and ends up malnourished, no matter how much he or she eats.
Signs and symptoms:
- No symptoms at all
- Digestive problems (abdominal bloating, pain, gas, constipation, diarrhea, pale stools, and weight loss).
- A severe blistering skin rash and sores in the mouth.
- Unexplained anemia or hepatitis.
- Musculoskeletal problems (muscle cramps, joint, and bone pain) and defects in dental enamel.
- Growth problems and failure to thrive (in children). This is because they cannot absorb the nutrients.
- Tingling sensation in the legs (caused by nerve damage and low calcium).
When to see a doctor?
Consult your doctor if you have diarrhea or digestive discomfort that lasts for more than two weeks. Consult your child's doctor if your child is pale, irritable or failing to grow or has foul-smelling, bulky stools. Be sure to consult your doctor before trying a gluten-free diet. If you stop or even reduce the amount of gluten you eat before you're tested for celiac disease, you can change the test results. Celiac disease tends to run in families. If someone in your family has the condition, ask your doctor if you should be tested.
سیلیک کا مرض(celiac disease):
یہ بیماری گلوٹن سے الرجی کی وجہ سے ہوتی ہے ، جو کہ ایک پروٹین ہے اور 3 قسم کے اناج میں پایا جاتا ہے: گندم ، جو اور رائی۔ گلوٹن آنتوں میں سوزش کراتا ہے اور چھوٹی آنت کے استر پر باریک بالوں جیسے ٹشو کو نقصان پہنچاتا ہے۔ کھانے سے غذائی اجزاء ان ہی ٹشو کے ذریعے ہضم ہوتے ہیں۔ اگر اس کو نقصان پہنچتا ہے تو ، مریض غذائی اجزاء کو ہضم نہیں کرسکتا اور کم غذائیت کا شکار ہوجاتا ہے ، چاہے وہ کتنا ہی کھائے۔
نشانات و علامات
- ہو سکتا ہے کوئی علامات بالکل نہیں ہو۔
- نظام ہاضمے کے مسائل (پیٹ پھولنا، درد، گیس، قبض، ڈائیریا، پیلا پاخانہ اور وزن میں کمی)۔
- جلد پر خارش والے چھالے اور منہ میں زخم۔
- خون کی کمی یا ہیپاٹائٹس۔
- پٹھوں کے مسائل (پٹھوں میں درد ، جوڑوں اور ہڈیوں میں درد) اور دانتوں کے مسائل۔
- نشوونما کے مسائل اور وزن اور قد میں عمر کے حساب سے کمی (بچوں میں)۔ اس کی وجہ یہ ہے کہ وہ غذائی اجزاء کو ہضم نہیں کر سکتے۔
- ٹانگوں میں سوئیاں چبھنے کا احساس (عصابی نقصان اور کم کیلشیم کی وجہ سے)۔
ڈاکٹر سے کب ملنا ہے
اپنے ڈاکٹر سے رجوع کریں اگر آپ کو ڈائیریا یا ہاضمے کی تکلیف ہے اور دو ہفتوں سے زائد عرصے تک جاری رہتی ہے۔ اپنے بچے کے ڈاکٹر سے رجوع کریں اگر آپ کے بچے کی رنگت پیلی ہو ، چڑچڑا ہو یا صحیح نشوونما نہ ہو رہی ہو یا بدبو دار اور بھاری پاخانہ ہو۔ گلوٹن سے پاک غذا آزمانے سے پہلے اپنے ڈاکٹر سے ضرور مشورہ کریں۔ اگر آپ سیلیک بیماری کے ٹیسٹ سے پہلے گلوٹین کی مقدار کو روکتے ہیں یا کم کرتے ہیں تو ، آپ ٹیسٹ کے نتائج تبدیل ہو سکتے ہیں۔ Celiac بیماری موروثی ہے۔ اگر آپ کے خاندان میں کسی کو یہ بیماری ہے تو اپنے ڈاکٹر سے رابطہ کہ کیا آپ کو ٹیسٹ کی ضرورت ہے ۔
Doctors to consult (Gastroenterologist):
Dr. Zulqarnain Khan Haider, Dr Inamullah Khan, Prof. Dr. Qurratul Ain Hyder
Note: Click the Doctor's name to make an appointment.
Reference:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/celiac-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20352220
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coeliac-disease.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Carpal-Tunnel-Syndrome-Fact-Sheet