Gallstones are more common in women than in men. They are also more common in overweight people and people with a family history of gallstones.
There is no single cause of gallstones. In some people, the liver produces too much cholesterol. This can result in the formation of cholesterol crystals in bile that grow into stones. In other people, gallstones form because of changes in other components of bile or because the gallbladder does not empty normally.
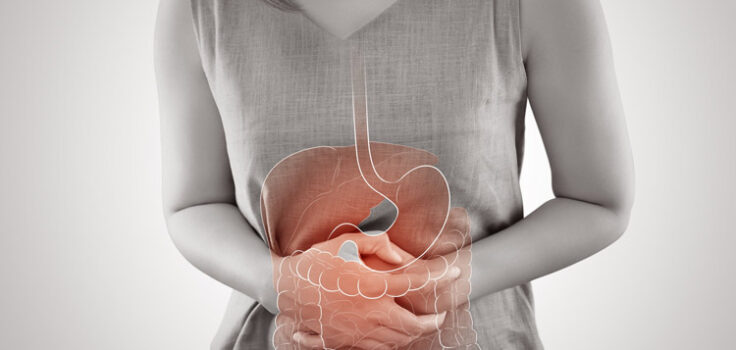
The gallbladder lies under the liver on the right side of the upper tummy (abdomen). It is like a pouch that comes off the main bile duct and fills with bile. It is a 'reservoir' which stores bile. The gallbladder squeezes (contracts) when we eat. This empties the stored bile back into the main bile duct. The bile passes along the remainder of the bile duct into the first part of the gut, known as the duodenum.
Signs and symptoms
In approximately 70 percent of cases, gallstones cause no symptoms. The symptoms of gallstones may include:
- pain in the abdomen and back. Pain is generally infrequent, but severe
- increase in abdominal pain after eating a fatty meal
- jaundice
- fever and pain, if the gallbladder or bile duct becomes infected
When to see a doctor?
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you.
Seek immediate care if you develop signs and symptoms of a serious gallstone complication, such as:
- Abdominal pain so intense that you can't sit still or find a comfortable position
- Yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes (jaundice)
- High fever with chills
پتے کی پتھری:
پتے کی پتھری مردوں کے مقابلے خواتین میں زیادہ عام ہے۔ یہ ایسے لوگوں میں زیادہ عام ہے کہ جن کا وزن زیادہ ہو یا خاندان میں پتھریوں کی بیماری پائی جاتی ہو۔
پتھری کی کوئی ایک وجہ نہیں ے۔ کچھ لوگوں میں ، جگر بہت زیادہ کولیسٹرول پیدا کرتا ہے جو کہ بائل میں کولیسٹرول کے کرسٹل بننے کا سبب بنتا ہے، یہ کرسٹل پھر پتھری کی شکل دھار لیتے ہیں۔ کچھ لوگوں میں بائل کے اجزاء میں بدلاؤ کی وجہ سے پتھریاں بنتی ہیں۔ یا اس وجہ سے کہ پتہ صحیح سے خالی نہیں ہو پاتا ہے۔
ِِپِتہ جگر کے نیچے اوپری پیٹ کے دائیں طرف پایا جاتا ہے۔ یہ ایک تھیلی کی طرح ہے جو مرکزی پتوں کی نالی (بائل ڈکٹ)سے نکلتا ہے اور اس میں بائل ( ایک طرح کا پانی) بھرا ہوا ہوتا ہے۔ یہ 'ذخیرہ' ہے جو بائل کو محفوظ کرتا ہے۔ جب ہم کھانا کھاتے ہیں تو پِتہ نچوڑتا ہے۔ یہ ذخیرہ شدہ بائل کو واپس مرکزی پتہ (بائل ڈکٹ) کی نالی میں خالی کرتا ہے۔ بائل، بائل ڈکٹ کے ساتھ آنت (گٹ) کے پہلے حصے میں جاتا ہے جسے گرہنی کے نام سے جانا جاتا ہے۔
پتھری کی علامات
تقریباً 70 فیصد معاملات میں ، پتھری کی کوئی علامت نہیں ہوتی ہے۔ پتھری کی علامات میں یہ شامل ہیں:
پیٹ اور کمر میں درد ، درد عام طور پر کبھی کبھار ہوتا ہے ، لیکن شدید ہوتا ہے۔
چکنائ والی غذا کھانے کے بعد پیٹ کے درد میں شدت کے ساتھ اضافہ
یرقان
پِتے اور پِتے کی نالی(بائل ڈکٹ) میں انفیکشن ہونے کی صورت ميں بخار اور درد کی کیفیت
ڈاکٹر سے کب ملنا ہے؟
اگر آپ کو کوئی علامات ہیں جو آپ کو پریشان کرتی ہیں تو ڈاکٹر سے ملاقات کریں ۔
اگر آپ کو ان علامات میں سے پتھری کی پیچیدہ علامات ظاہر ہوتی ہیں تو فوری ڈاکٹر سے رجوع کریں۔
پیٹ میں درد اتنا شدید ہے کہ آپ سیدھا نہیں بیٹھ سکیں اور نہ ہی کسی اور آرام دہ پوزیشن میں بیٹھ سکیں۔
آپ کی جلد اور آنکھوں کا پیلا ہو۔ یرقان
سردی لگنے کے ساتھ تیز بخار ہو
Doctors to consult (Urologist):
Asst.Prof. Dr. Mohsin Naveed, Dr. Nina Munir, Dr Shahid Hussain, Dr. Zafar Abbas
Note: Click the Doctor's name to make an appointment.
Reference:
https://patient.info/digestive-health/gallstones-and-bile
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gallstones/symptoms-causes/syc-20354214
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/gallbladder-gallstones-and-surgery